
Originally published in the New York Times ‘The Morning’ by German Lopez
Earlier this year, millions of Americans got a notice: Your food budget is about to be cut, potentially by hundreds of dollars a month. Here are some tips on how you can manage. You can’t appeal.
The notices signaled the coming end of a federal increase in food stamps that started in the early days of the pandemic, when unemployment spiked and lawmakers feared that hunger would, too.
The cuts come at a particularly bad time for low-income Americans. Grocery prices increased 10 percent over the past year, according to data released this week. It amounts to a one-two punch: The country’s neediest have less aid to pay for food as it’s getting more expensive.
The big question is what happens now. Some experts have warned that the country is approaching a “hunger cliff,” with the number of Americans going hungry likely to spike this spring. To buy food, other families may have to use money that would otherwise have gone to rent or other bills — and fall behind on those payments.
The stress on family food budgets represents a tangible example of how a recent rise in the nation’s poverty rate is affecting people’s lives. The poverty rate fell sharply in 2021 — to 7.8 percent by one measure, from 11.8 percent in 2019 — thanks mostly to economic relief laws that Congress passed in response to Covid. But Congress has let many provisions expire, and the poverty rate rose in 2022 as a result.
“It is a very large and abrupt change,” said Ellen Vollinger of Food Research and Action Center, an advocacy group. “The hardship will fall on these families.”
Emergencies’ End
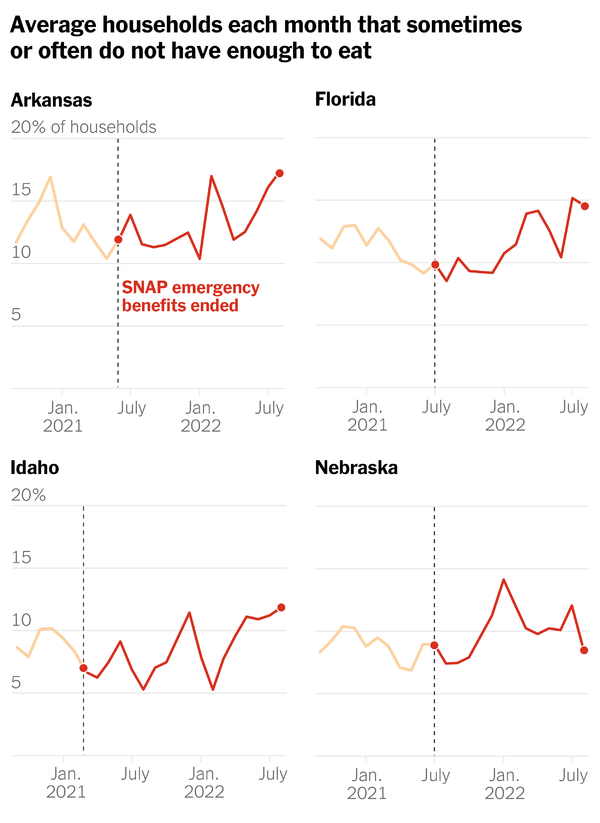
We already have a glimpse of how the food stamp cuts will play out. This month’s cuts ended the expanded benefits in the 32 states that still had them, but 18 states had already revoked their extra benefits. In those 18 states, food insecurity, which measures insufficient access to food, rose more quickly than in states that kept the benefits, researchers at Northwestern University and the Jain Family Institute found.
These charts from my colleague Ashley Wu show the trend in four of the states that cut food stamps earlier. The data fluctuates. But generally, more households struggled to get enough to eat after the cuts:
The situation could get worse. When many of those 18 states cut benefits, food prices were rising less quickly than they have been more recently. The government adjusts food stamps for inflation, but only once a year, in October. So if prices keep rising quickly, the real value of food stamps will fall behind for the next several months.
Food stamp benefits will still be higher than they were before the pandemic because the Biden administration separately increased them in 2021. But those increases don’t outweigh the end of emergency benefits for many recipients, meaning their food budgets will still decrease.
Some conservatives say the warnings are overblown. Angela Rachidi of the American Enterprise Institute argued that the effects of the emergency benefits were exaggerated and that they were always supposed to be temporary.
Return to normal
Ultimately, the food stamp cuts will probably push more people — potentially millions more — into poverty, said Megan Curran of the Center on Poverty and Social Policy at Columbia University. That increase will largely erase what remains of recent years’ progress on the issue.
In that sense, the food stamp cuts fit into a broader story: During the pandemic, the U.S. expanded its safety net to prevent the worst outcomes of a crashing economy. Those policies worked to keep people out of poverty. But now that the economy has recovered from the initial pandemic shock, Congress is letting the safety net shrink back down. And poverty is rising back to where it once was.